Isotech offers a full range of Fiber, C02, UV, Green, MOPA, Nanosecond, Picosecond and Femtosecond laser systems for marking, cutting and welding of many substrates. Isotech offers both standard systems as well as fully automated or custom systems depending on your specific requirements. Integrated, automated solutions with conveyors, palletized pick and place, rotary dial tables, hoppers, and...

At Cincinnati Incorporated, we present ourselves as a dedicated manufacturer of industrial lasers engineered to deliver the speed, precision, and long-term reliability required in modern fabrication environments. We design our laser cutting systems to handle everything from thin-gauge materials to heavy plate with consistent edge quality, stable power delivery, and efficient cutting performance.

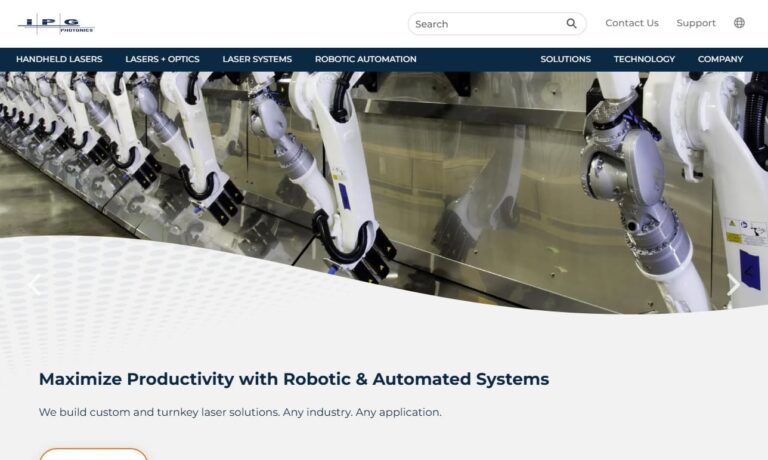
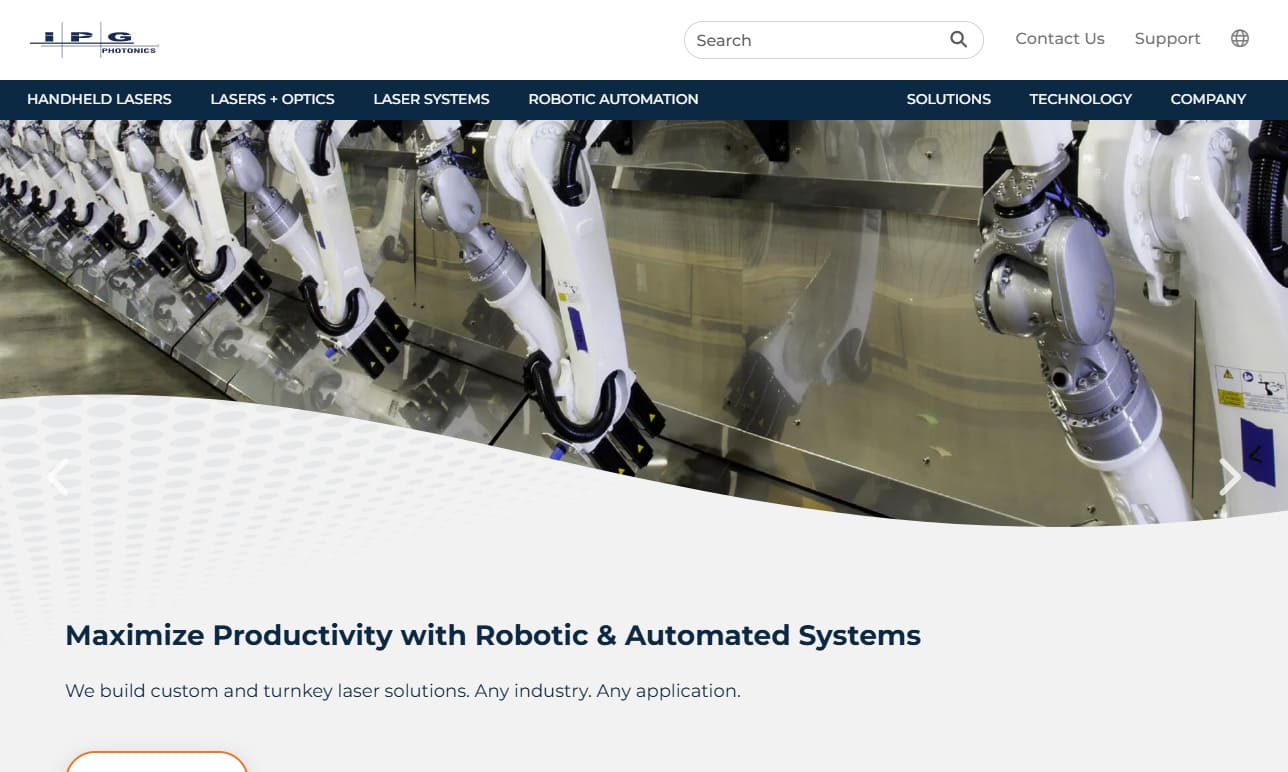
At IPG Photonics Corporation, we present ourselves as a global leader in the development and manufacturing of high-performance lasers designed to bring unmatched precision, efficiency, and reliability to industrial, scientific, and advanced technological applications. We focus on engineering fiber lasers, amplifiers, and photonic solutions that deliver stable output, exceptional beam quality, and ...
Laser Marking Technologies LLC engineers laser systems for the medical, manufacturing, and automotive industries. We provide you cutting-edge technology at competitive prices. We are making innovative strides with fiber lasers, 3D printing tech, and automation capabilities that optimize manufacturing processes. Visit our site today to learn more about what our laser expertise can do for you.

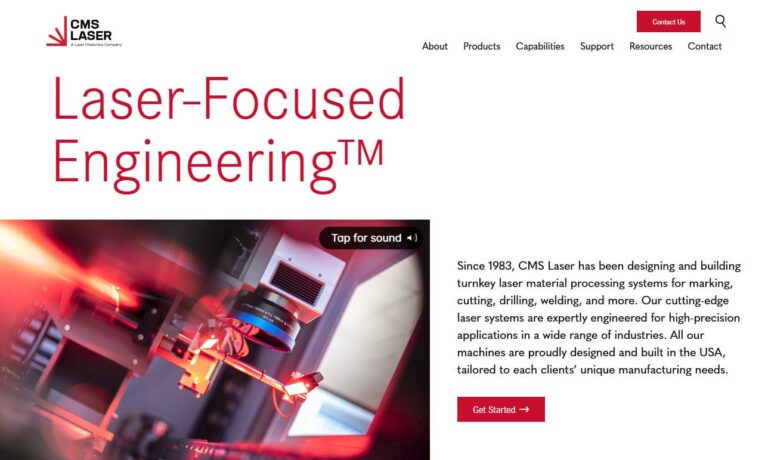
Control Micro Systems specializes in marking lasers. Our laser marking systems are built for marking metals, plastics, glass, electronics, medical devices and extrusions. Some of our other unique and versatile industrial lasers include laser engraving products and etching lasers.
If your business has a challenging component to mark on, our team at Automark will help you solve the problem. We supply laser and marking systems for a multitude of industries. Our team of engineers is ready and willing to tackle any of your challenging assignments. If you have any questions feel free to give us a call and a representative will speak with you today!

More Fiber Laser Manufacturers
Fiber Lasers: Technology, Applications, and Industry Insights
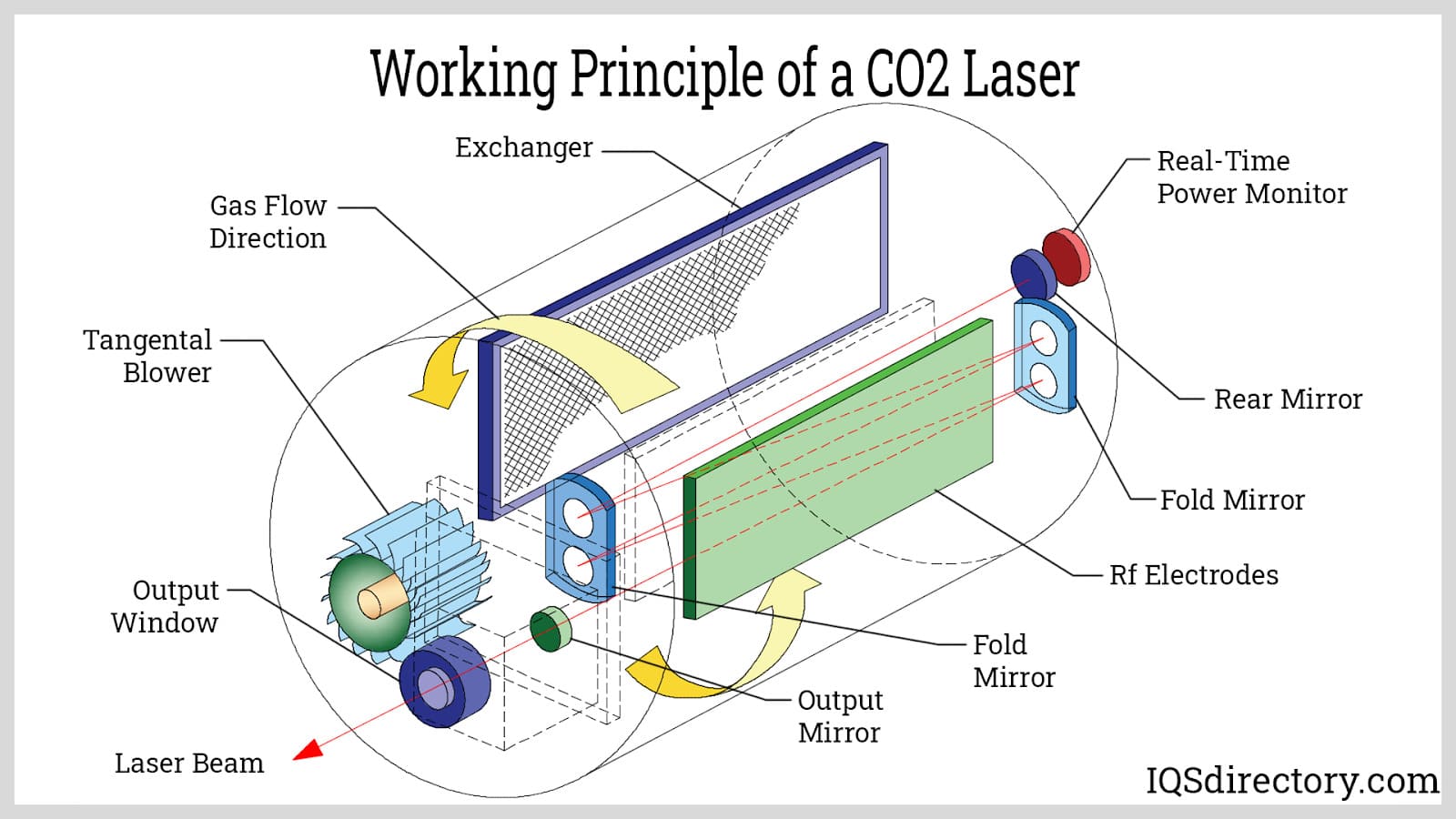
Fiber lasers have revolutionized the landscape of industrial laser technology by offering unmatched performance, precision, and versatility. These advanced lasers operate on principles similar to gas lasers, but with a key difference: part of the optical fiber itself serves as the resonating cavity where laser action occurs. This unique architecture enables manufacturers to create compact fiber laser systems, as the flexible fiber can be coiled or bent to conserve space without sacrificing beam quality or efficiency.
What Is a Fiber Laser and How Does It Work?
At its core, a fiber laser consists of a laser system, a length of flexible quartz or glass fiber doped with rare-earth elements (such as ytterbium, erbium, or neodymium), and a laser diode pump source. The process relies on total internal reflection (TIR) to propagate light through the fiber. When a powerful pump light is introduced through a semi-transparent mirror, it excites the dopant atoms within the core, causing them to emit coherent, near-monochromatic light. This light is then amplified by thousands of reflections within the fiber, resulting in a high-intensity, focused laser beam that can be delivered over long distances with minimal loss.
Unlike traditional solid-state or gas lasers, fiber lasers are highly efficient, producing minimal heat and requiring less maintenance. Their robust design eliminates the risk of misalignment, contamination, and the need for frequent recalibration, making them a preferred choice for demanding industrial and scientific environments.
Key Advantages and Benefits of Fiber Lasers
- Exceptional Beam Quality: Fiber lasers deliver a high-quality, diffraction-limited output that enables precise cutting, welding, and engraving, especially in microfabrication and electronics manufacturing.
- Compact and Flexible Design: The ability to bend and coil the fiber allows for space-saving integration in production lines and laboratory setups.
- High Electrical Efficiency: With wall-plug efficiencies approaching 40%, fiber lasers significantly reduce operating costs and energy consumption compared to CO2 or lamp-pumped lasers.
- Low Maintenance Requirements: The all-fiber construction minimizes the need for realignment and routine servicing, boosting uptime and productivity.
- Multi-Wavelength Capability: Fiber lasers can emit at multiple wavelengths, enabling advanced techniques like wavelength multiplexing and multi-material processing.
- Long Operational Life: Thanks to their solid-state construction, fiber lasers can operate reliably for tens of thousands of hours, even in harsh environments.
- Vibrational Stability: The fiber-based architecture is inherently resistant to vibration, ensuring consistent output in industrial settings.
- Scalability and Power Range: Fiber lasers are available in a wide range of output powers, from a few milliwatts for precision marking to multi-kilowatt systems for thick metal cutting and welding.
Fiber Laser Applications Across Key Industries
Fiber lasers are used in a multitude of sectors due to their versatility and high performance. Below is a breakdown of the most prominent fiber laser applications:
Industrial Manufacturing and Metal Processing
One of the largest markets for fiber lasers is industrial manufacturing, where they are critical for laser cutting, welding, engraving, drilling, and marking. Their ability to cut through a wide range of metals—including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and titanium—as well as plastics and composite materials makes them indispensable for:
- Automotive manufacturing: Precision cutting and joining of chassis, body frames, gears, and exhaust systems.
- Aerospace and defense: Fabrication of lightweight, high-strength components for aircraft, satellites, and missile systems.
- Jewelry and watchmaking: Fine engraving and intricate cutting for precious metals and personalized designs.
- Electronics and semiconductor fabrication: Micro-welding, ablation, and scribing for PCB production, microchips, and MEMS devices.
- General manufacturing: Creation of complex parts, tools, and custom assemblies with high repeatability.
Medical and Life Sciences
In the medical sector, fiber lasers have enabled new advancements in precision surgery, diagnostics, and therapy. They are widely employed for:
- Photo-activation of light-sensitive drugs (photodynamic therapy): Used in cancer treatment and dermatology.
- Laser surgery and tissue ablation: Minimally invasive procedures for eye surgery (LASIK), vascular treatments, and more.
- Medical device manufacturing: Fabrication, welding, and marking of stents, implants, and surgical tools.
- Spectroscopy and diagnostic imaging: High-resolution analysis of biological samples and tissues.
Looking to integrate fiber lasers in your medical practice or device manufacturing process? Assess the wavelengths, pulse duration, and regulatory compliance required for your specific application.
Telecommunications and Optical Communications
Fiber lasers play a key role in the development and support of telecommunications networks and optical communication systems such as:
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM): Fiber lasers act as precise light sources for multiplexing multiple signals on a single fiber.
- High-speed optical receivers: Providing stable, narrow-linewidth sources for signal transmission.
- Long-haul data transmission: Amplification of signals over several kilometers without significant loss.
Other Notable Applications
- Food processing and packaging: Non-contact marking, scribing, and cutting for traceability and branding.
- 3D printing and additive manufacturing: Sintering and melting of metal powders for rapid prototyping and production.
- Solar cell and battery manufacturing: Precision laser scribing, drilling, and welding for photovoltaic panels and energy storage devices.
- Scientific research and spectroscopy: Tunable wavelength output for advanced laboratory experiments.
Types of Fiber Lasers and Selection Criteria
Choosing the right fiber laser system depends on several factors, including the specific application requirements, material properties, and desired output. Major types of fiber lasers include:
- CW (Continuous Wave) Fiber Lasers: Best suited for applications requiring steady, high-power output, such as cutting and welding thick materials.
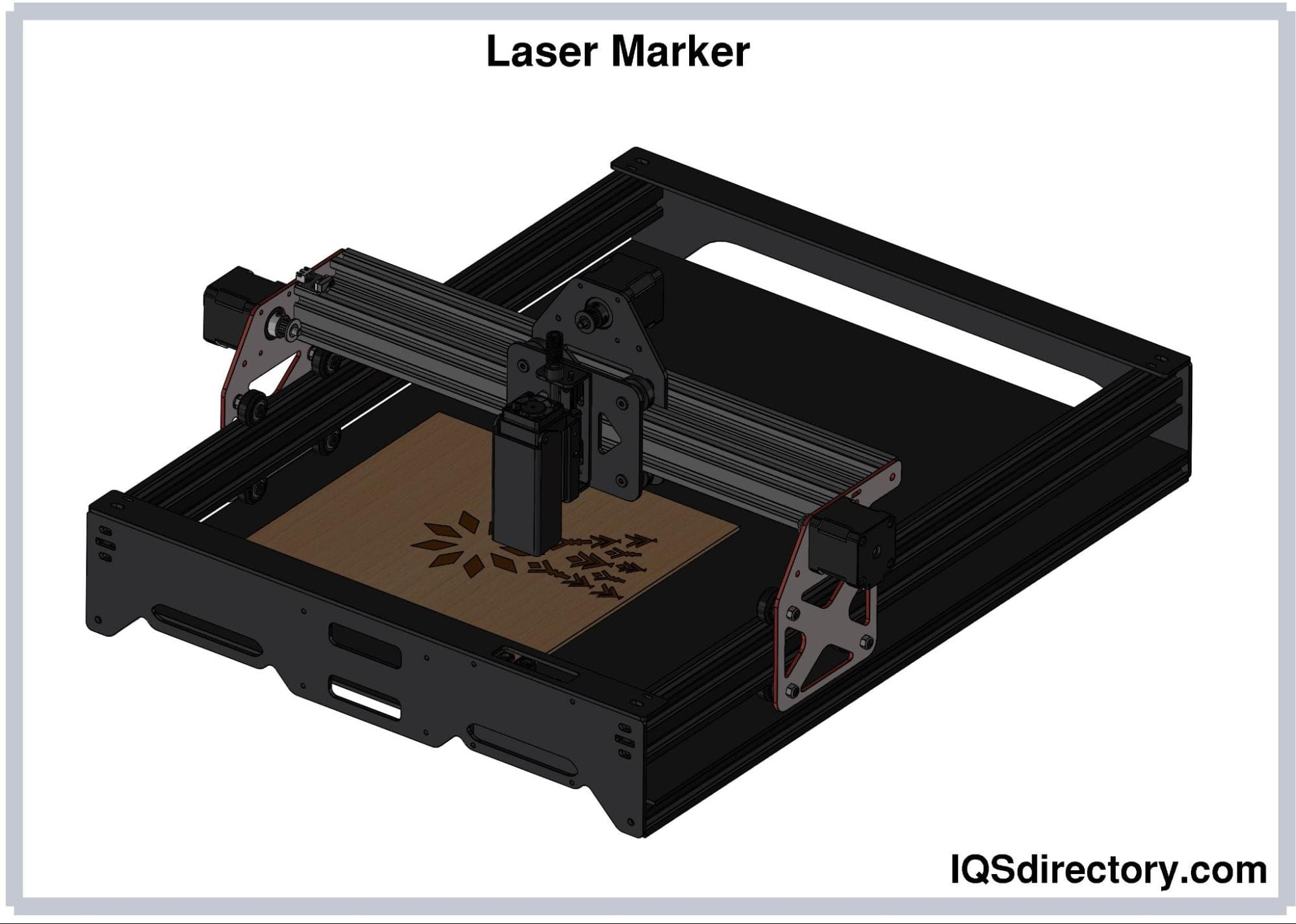
- Pulsed Fiber Lasers: Ideal for marking, engraving, micromachining, and applications where heat-sensitive materials are involved.
- Ultrafast (Femtosecond and Picosecond) Fiber Lasers: Deliver extremely short pulses for high-precision microfabrication, glass processing, and medical imaging.
- MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) Fiber Lasers: Provide adjustable pulse durations and repetition rates for versatile marking and surface treatment tasks.
- Single-mode vs. Multi-mode Fiber Lasers: Single-mode lasers offer superior beam quality and focusability, whereas multi-mode lasers provide higher power for bulk processing.
Curious about which fiber laser technology fits your application? Ask yourself:
- What materials will I process (metals, plastics, ceramics, composites)?
- What thickness and precision do I require?
- Do I need high-speed throughput or fine detail?
- Is portability or system integration important?
- What is my budget for capital investment and operating costs?
How Fiber Lasers Compare to Other Laser Technologies
When evaluating fiber lasers vs. CO2 lasers, Nd:YAG lasers, or diode lasers, several factors set fiber lasers apart:
- Efficiency: Fiber lasers convert more electrical power into laser light, reducing energy costs.
- Maintenance: No mirrors or delicate optics to align; fiber delivery is robust against dust and vibration.
- Beam Quality: Superior focusability leads to cleaner cuts and finer engraving.
- Operational Cost: Longer lifespans and fewer consumables lower total cost of ownership.
- Material Compatibility: Fiber lasers can process highly reflective metals that challenge other systems.
Key Considerations When Buying a Fiber Laser System
Selecting the right fiber laser machine is a strategic investment. Here are the primary decision factors to evaluate:
- Power Output: Higher wattage fiber lasers enable faster processing and thicker material cutting, but may increase upfront cost.
- Pulse Characteristics: Adjustable pulse modes and durations enhance flexibility for different tasks.
- Beam Delivery: Look for systems with integrated beam delivery optics, auto-focus heads, and motion control.
- Cooling Requirements: Some high-power fiber lasers require water cooling; others are air-cooled for simplicity.
- Automation and Integration: Seamless integration with robotics and Industry 4.0 systems can boost productivity.
- Software and Control Interface: User-friendly controls and CAD/CAM compatibility streamline workflow.
- Service and Support: Choose a supplier with proven support, training, and spare parts availability.
- Regulatory and Safety Compliance: Ensure the system meets laser safety standards (such as IEC 60825-1, FDA/CDRH, or local regulations).
Ready to take the next step in your research? Request a demonstration, download technical datasheets, or chat with our fiber laser experts for tailored guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fiber Lasers
- What is the lifespan of a fiber laser? Modern fiber lasers can operate for 50,000 to 100,000 hours with minimal maintenance, significantly outlasting most conventional lasers.
- Can fiber lasers cut both metals and non-metals? While fiber lasers excel at cutting metals (including reflective materials like copper and brass), certain plastics and organic materials may require different wavelengths or alternative laser sources for optimal results.
- What safety precautions are needed? Always operate fiber lasers in accordance with local safety regulations, using appropriate eyewear, enclosures, and interlocks.
- How does a fiber laser differ from a diode laser? Fiber lasers use a doped fiber as the gain medium and are typically pumped by diodes, offering higher beam quality, stability, and power scalability.
- Is it possible to upgrade my existing CNC machine with a fiber laser? Many CNC and automation platforms can be retrofitted with fiber laser heads, provided the motion system is compatible and can handle the required power levels.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in Fiber Laser Technology
The fiber laser market continues to evolve, driven by advances in materials science, photonics, and digital manufacturing. Key innovations shaping the future of fiber lasers include:
- Higher Power and Beam Shaping: New designs enable multi-kilowatt output and programmable beam profiles for optimized material interaction.
- Green and Ultraviolet Fiber Lasers: Frequency conversion techniques expand applications to solar, electronics, and medical imaging.
- Integration with AI and IoT: Smart monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive process control are improving uptime and quality.
- Compact, Portable Fiber Lasers: Handheld and mobile systems are opening new opportunities in field repair, art restoration, and on-site processing.
- Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: Highly efficient fiber lasers reduce carbon footprint, power consumption, and hazardous waste in industry.
Conclusion: Why Choose Fiber Lasers?
Fiber lasers are setting new standards in industrial, medical, and scientific applications. Their combination of precision, reliability, and cost effectiveness makes them the technology of choice for manufacturers, researchers, and service providers worldwide. Whether you are upgrading your production line, developing the next generation of medical devices, or advancing optical communication infrastructure, a fiber laser system delivers the performance and flexibility required to stay ahead in today’s competitive landscape.
Ready to learn more or take the next step? Explore our in-depth guides, request a quote, or book a demonstration to see firsthand how fiber lasers can transform your workflow and boost your ROI.






 Automation Equipment
Automation Equipment Car Wash Equipment
Car Wash Equipment Centrifuges
Centrifuges Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic Presses Lasers
Lasers Machinery Rebuilders
Machinery Rebuilders Paint Finishing Equipment
Paint Finishing Equipment Tube Forming Machines
Tube Forming Machines Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services